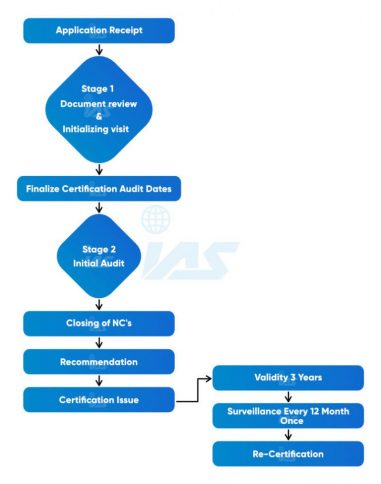
Understanding ISO Audit Basics: Key Elements and Objectives
ISO audits play a crucial role in ensuring organizations adhere to the established international standards for quality management systems. To grasp the significance of ISO audits, it is essential to understand their key elements and objectives.
An ISO audit primarily aims to evaluate an organization’s compliance with the relevant ISO standards, such as ISO 9001 for quality management. It involves a systematic review of processes, procedures, and documentation to determine their conformity with the defined requirements. The audit also assesses the effectiveness and efficiency of the organization’s quality management system.
During an ISO audit, auditors examine various aspects, including the organization’s documented procedures, process controls, risk management practices, record-keeping, and continual improvement efforts. They may conduct interviews with employees, review documentation, and observe operations to gather evidence of compliance.
The objectives of an ISO audit extend beyond mere compliance. They include identifying areas for improvement, validating the effectiveness of the organization’s quality management system, and promoting a culture of continuous improvement. The audit results serve as a foundation for enhancing processes, addressing non-conformities, and driving organizational excellence.
By understanding the key elements and objectives of ISO audits, organizations can approach the audit process proactively. They can ensure their quality management system is well-documented, processes are effectively implemented, and employees are trained to adhere to the established standards. This understanding also enables organizations to view ISO audits as opportunities for growth and improvement rather than mere compliance exercises.
In conclusion, comprehending the basic elements and objectives of ISO audits empowers organizations to approach the audit process strategically. It allows them to align their quality management systems with ISO standards, identify areas for improvement, and foster a culture of continuous enhancement.
Preparing for an ISO Audit: Essential Steps and Checklist
Preparing for an ISO audit is a crucial step to ensure a smooth and successful assessment of your organization’s compliance with the relevant ISO standards. By following essential steps and using a comprehensive checklist, you can effectively navigate the audit procedure and increase the chances of a favorable outcome.
- Conduct a Gap Analysis: Start by performing a gap analysis to identify any areas where your current practices deviate from the requirements of the ISO standard. This analysis will help you pinpoint gaps and prioritize actions needed for compliance.
- Establish Documentation Controls: Ensure that your documentation, including policies, procedures, work instructions, and records, is up-to-date, accessible, and properly maintained. Implement a robust document control system that allows for easy retrieval and tracking of documents during the audit.
- Train and Educate Employees: Provide training to all employees on their roles and responsibilities in adhering to the ISO standards. This includes raising awareness of quality policies, promoting adherence to procedures, and fostering a culture of continuous improvement.
- Conduct Internal Audits: Regularly perform internal audits to assess your organization’s compliance and readiness for the ISO audit. Internal audits help identify areas of improvement and ensure that corrective actions are implemented in a timely manner.
- Perform a Mock Audit: Consider conducting a mock audit to simulate the actual ISO audit process. This exercise allows you to evaluate your preparedness, identify potential weaknesses, and make necessary adjustments before the official audit.
- Select Competent Auditors: Engage qualified and experienced auditors who possess a deep understanding of the ISO standard you are being audited against. Ensure they are impartial, objective, and have no conflicts of interest with your organization.
- Organize Documentation and Records: Prepare all relevant documentation and records required for the audit, such as quality manuals, procedures, process flowcharts, and evidence of corrective actions taken. Organize them in a systematic and easily accessible manner.
- Communicate and Coordinate: Maintain open lines of communication with auditors throughout the audit process. Clarify any questions or concerns they may have, and provide timely and accurate information.
- Conduct a Pre-Audit Review: Perform a comprehensive review of your organization’s readiness shortly before the audit. Verify that all necessary preparations are complete, and address any remaining gaps or issues.
By following these essential steps and utilizing a comprehensive checklist, you can significantly enhance your organization’s preparedness for an ISO audit. Being well-prepared not only increases the chances of a successful audit but also demonstrates your commitment to quality and continuous improvement.
Conducting a Successful ISO Audit: Best Practices and Techniques
Conducting a successful ISO audit requires careful planning, effective communication, and a systematic approach. Implementing best practices and employing proven techniques can help auditors and organizations navigate the audit procedure with confidence. Here are some key considerations for ensuring a successful ISO audit:
- Establish Clear Objectives: Clearly define the objectives and scope of the audit. Communicate the purpose of the audit to all stakeholders involved, ensuring a shared understanding of expectations and desired outcomes.
- Select Competent Auditors: Choose auditors who possess the necessary expertise, knowledge, and experience in the specific ISO standard being audited. Competent auditors understand the requirements of the standard and can effectively assess compliance.
- Plan the Audit Schedule: Develop a well-structured audit schedule that accounts for the availability of auditors and key personnel. Allocate sufficient time for each audit activity, including document review, interviews, and on-site observations.
- Communicate with the Organization: Establish open and transparent communication channels with the organization undergoing the audit. Provide clear instructions and guidance on the audit process, expectations, and documentation requirements. Foster a collaborative environment that encourages cooperation and facilitates the exchange of information.
- Conduct Thorough Document Review: Start the audit process with a comprehensive review of the organization’s documented procedures, policies, records, and other relevant documentation. Evaluate the alignment of these documents with the requirements of the ISO standard.
- Employ Effective Interview Techniques: During on-site visits, conduct interviews with personnel at various levels of the organization. Utilize effective interview techniques such as active listening, open-ended questions, and probing to gather accurate and valuable information.
- Practice Non-Destructive Observation: Observe the organization’s processes and activities without causing disruption. Use non-destructive observation techniques to evaluate the implementation and effectiveness of documented procedures in real-world scenarios.
- Maintain Objectivity and Impartiality: Ensure auditors maintain objectivity and impartiality throughout the audit process. Adhere to professional ethics and avoid conflicts of interest that may compromise the integrity of the audit.
- Provide Constructive Feedback: Offer clear and constructive feedback to the organization being audited. Identify non-conformities, areas for improvement, and best practices observed during the audit. Help the organization understand how to address identified gaps and enhance their quality management system.
- Follow-Up on Corrective Actions: After the audit, monitor the organization’s progress in addressing identified non-conformities and implementing corrective actions. Provide guidance and support as needed to ensure the organization achieves sustained compliance with the ISO standard.
By incorporating these best practices and techniques into the ISO audit process, auditors can enhance the effectiveness of their assessments, while organizations can leverage the audit as a catalyst for continuous improvement and quality excellence.
Addressing Non-Conformities: Strategies for Effective Corrective Actions
During an ISO audit, non-conformities may be identified, highlighting areas where an organization’s practices do not meet the requirements of the ISO standard. Effectively addressing these non-conformities is essential for maintaining compliance and driving continuous improvement. Here are some strategies for implementing effective corrective actions as part of the audit procedure:
- Identify Root Causes: Investigate the root causes of the identified non-conformities. Conduct a thorough analysis to determine the underlying factors contributing to the non-compliance. This analysis helps address the core issues rather than merely treating the symptoms.
- Prioritize Corrective Actions: Prioritize corrective actions based on their impact and significance. Address critical non-conformities that pose a high risk to the organization’s operations, customer satisfaction, or compliance with the ISO standard. Establish a systematic approach to address non-conformities based on their priority level.
- Develop Action Plans: Create detailed action plans for each non-conformity, outlining specific steps, responsibilities, and timelines for implementing corrective actions. Ensure that the action plans are realistic, achievable, and aligned with the organization’s resources and capabilities.
- Involve Cross-Functional Teams: Engage cross-functional teams in the corrective action process. Collaborative efforts involving employees from various departments can bring diverse perspectives and expertise to address non-conformities comprehensively.
- Monitor and Track Progress: Regularly monitor and track the progress of corrective actions. Establish mechanisms to measure the effectiveness of implemented actions in addressing non-conformities. This includes defining key performance indicators (KPIs) and conducting follow-up audits or reviews.
- Promote Continuous Improvement: View non-conformities as opportunities for improvement rather than failures. Encourage a culture of continuous improvement within the organization, where employees are empowered to identify and address potential non-conformities proactively.
- Communicate and Train: Communicate the identified non-conformities and the corresponding corrective actions to relevant stakeholders within the organization. Ensure that employees understand their roles and responsibilities in implementing the corrective actions. Provide training and support as needed to facilitate the successful implementation of corrective measures.
- Review and Learn from Non-Conformities: Conduct a systematic review of the effectiveness of implemented corrective actions. Identify lessons learned from the non-conformities and use this knowledge to enhance processes, procedures, and the overall quality management system.
- Document and Maintain Records: Document all corrective actions taken and maintain records as evidence of compliance with the ISO standard. These records serve as a reference for future audits and demonstrate the organization’s commitment to continual improvement.
By implementing these strategies for effective corrective actions, organizations can address non-conformities promptly, enhance their quality management systems, and foster a culture of continuous improvement.